Diverting non-haem iron catalysed aliphatic C–H hydroxylations towards desaturations
Marinus A. Bigi, Sean A. Reed, M. Christina White
Nature Chemistry,
2011, 216-222; 10.1039/C0CS00217H
01/2011
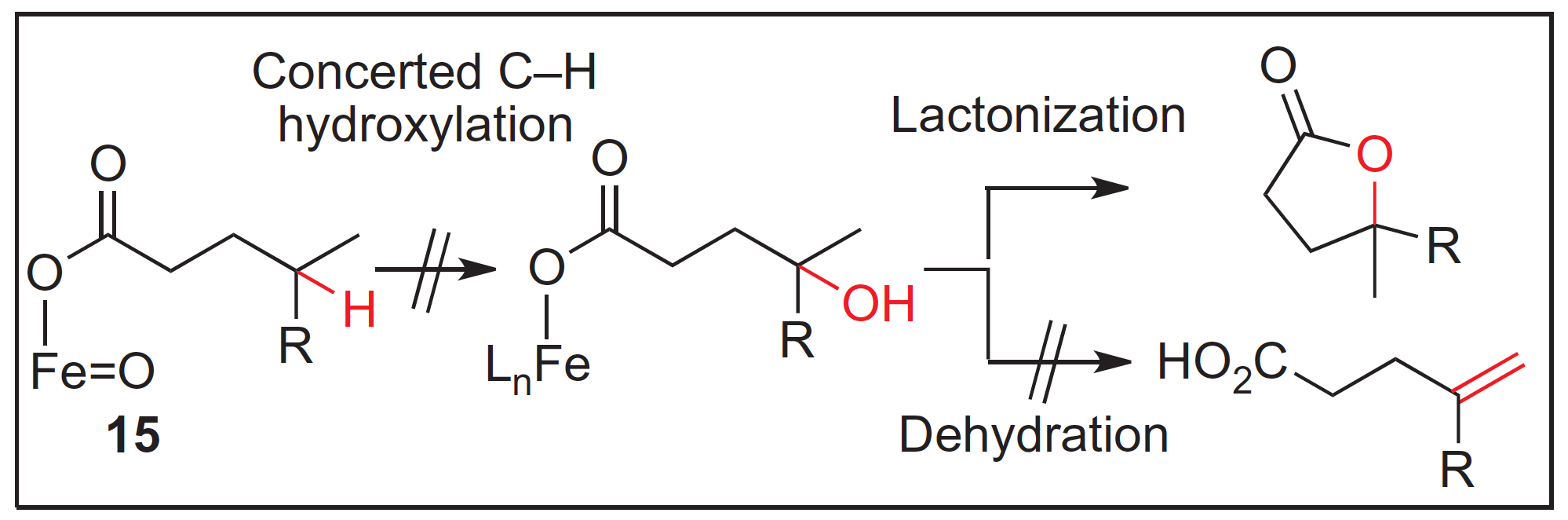
Taking inspiration from Nature the White group present non-heme Iron catalysts capable of mixed hydroxylation/desaturation of aliphatic C–H bond activity. Nature has evolved a series of carboxylated-ligated non-heme iron enzymes capable of promoting oxidative reactions of alkanes in a selective fashion. This ability and the observations garnered from the enzymes have guided the development of the Fe(PDP) catalyst by the White group.
This report describes the reaction of this catalyst system with a range of simple small molecules and more advanced molecular architectures such as natural products. It sheds light on the various structural features of the substrates that impact the reactivity and selectivity of this catalyst.
These results not only inform the design and evolution of this catalyst system but also open the door to the intriguing prospect of using C–H functionalization to adapt and change natural products to perhaps modify and improve their biological activity, potentially providing new leads for therapeutic targets.