Insight into Mechanistic Features of Ruthenium(II)-Pybox Catalyzed C-H Amination
Musaev, D. G., Blakey, S. B.
Organometallics,
2012, 4950-4961; 10.1021/om300153q
06/2012
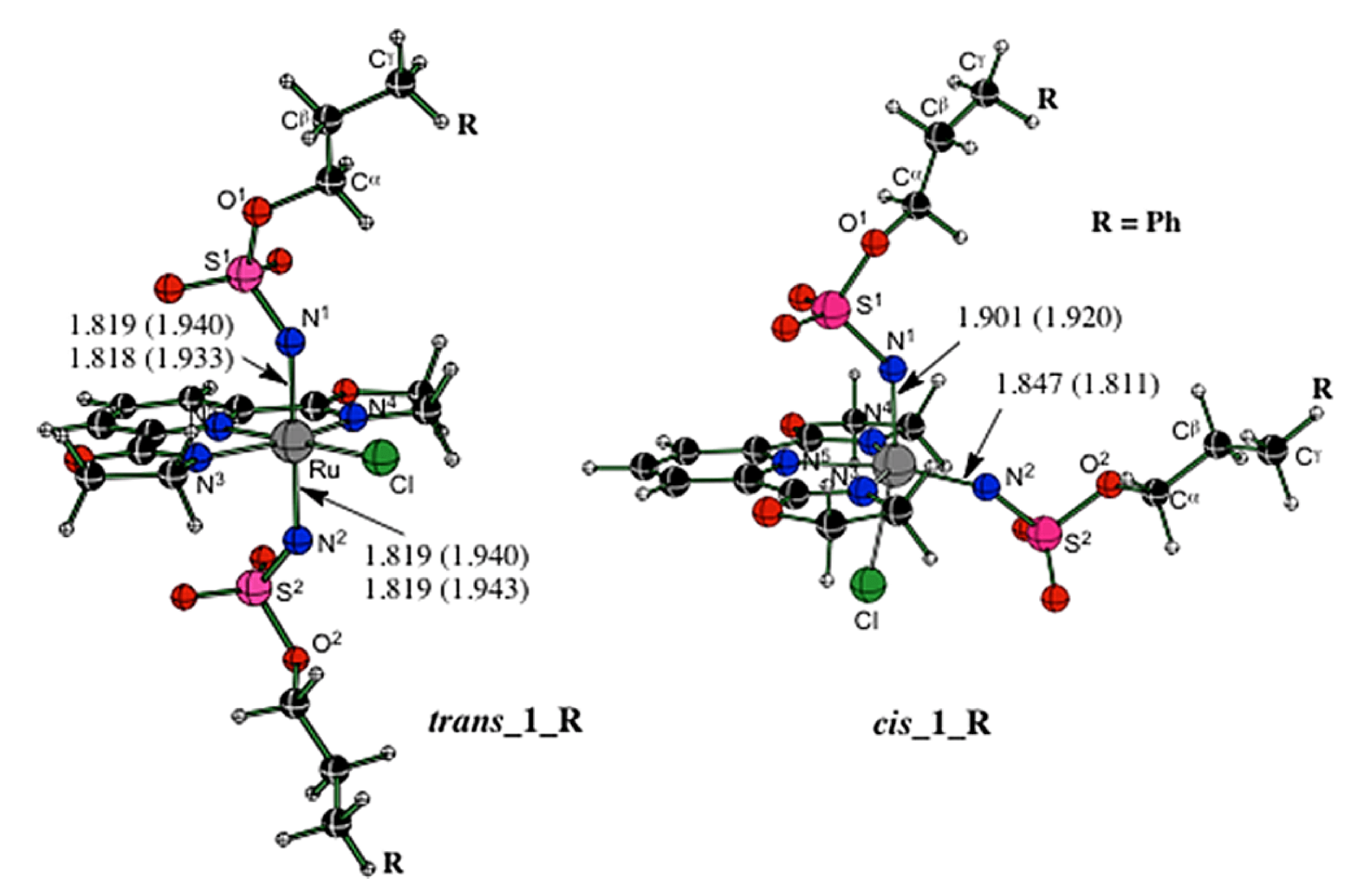
Development of new catalyst systems is essential to the expansion of the scope of transformations possible in C–H functionalization. This collaborative report from the Musaev and Blakey groups details a study into the development of a new class of ruthenium-based catalysts.
The mechanisms and controlling factors of intra- and intermolecular C–H bond amination catalyzed by cationic bis-imido complex [(Pybox)Ru(NSO3CH2CH2CH2R)2Cl]+ (1_R, where R = H, Ph) were elaborated at the density functional level.
Experimental and theoretical studies were used to learn more about the mechanism present in this transformation.