Cafestol to Tricalysiolide B and Oxidized Analogues: Biosynthetic and Derivatization Studies Using Non-heme Iron Catalyst Fe(PDP)
Bigi, M. A., Liu, P., Zou, L., Houk, K. N., White, M. C.
Synlett,
2012, 2768-2772; 10.1055/s-0032-1317708
11/2012
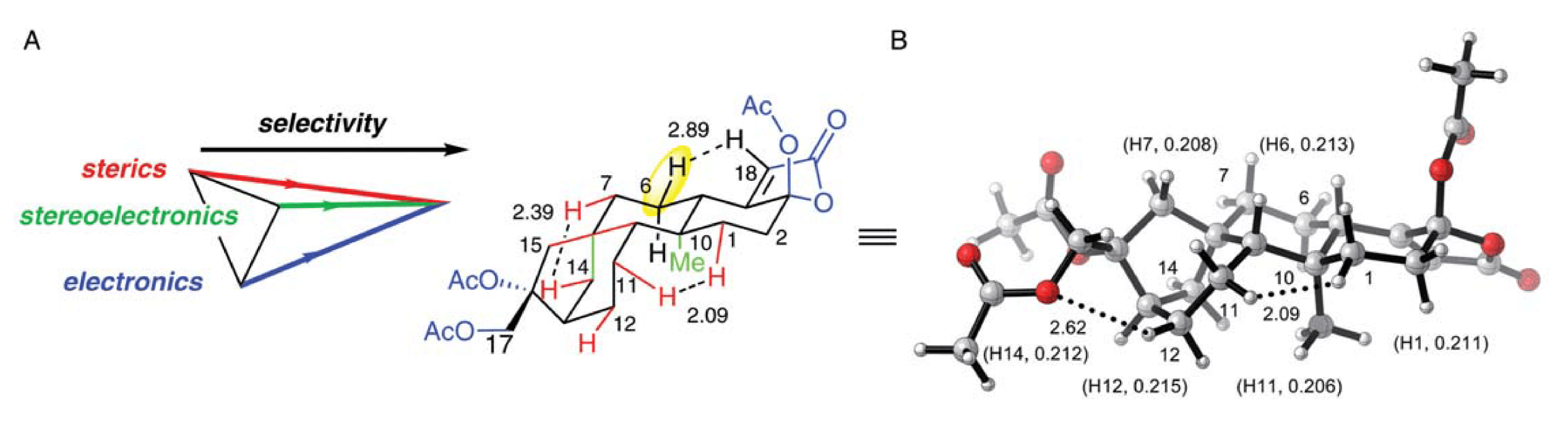
The tricalysiolides are a recently isolated class of di-terpene natural products featuring the carbon backbone of the well-known coffee extract, cafestol. Herein we validate the use of our non-heme iron complex, Fe(PDP), as an oxidative tailoring enzyme mimic to test the proposal that this class of natural products derives from cafestol via cytochrome P-450-mediated furan oxidation. Thereafter, as predicted by computational analysis, C–H oxidation derivatization studies provided a novel 2° alcohol product as a single diastereomer.