Site-selective bromination of sp3 C–H bonds
Shyam Sathyamoorthi, Shibdas Banerjee, J. Du Bois, Noah Z. Burns and Richard N. Zare
Chemical Science,
2018, 9, 100; DOI:10.1039/C7SC04611A
11/2017
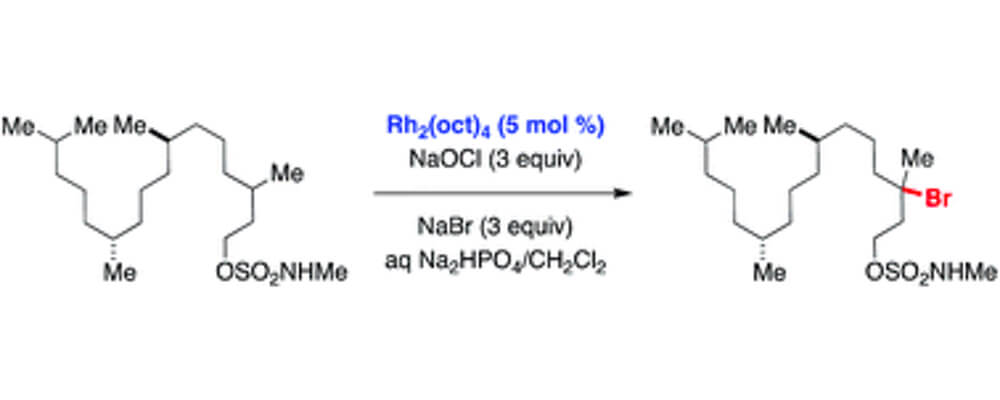
This collaborative report from the Du Bois and Zare labs describes the investigation of a dirhodium-catalyzed method for converting sp3 C–H bonds to C–Br using an N-methyl sulfamate directing group.
The reaction employs Rh2(oct)4 and a mixture of NaBr and NaOCl and is performed in aqueous solution open to air. For all sulfamates examined, oxidation occurs with high selectivity at the γ-carbon, affording a uniquely predictable method for C–H bond halogenation. Results from a series of mechanistic experiments suggest that substrate oxidation likely proceeds by a radical chain process. Initial formation of an N-halogenated sulfamate followed by Rh-mediated homolysis generates an N-centered radical, which serves as the active oxidant.