Quantitative Modeling of Bis(pyridine)silver(I) Permanganate Oxidation of Hydantoin Derivatives: Guidelines for Predicting the Site of Oxidation in Complex Substrates
Amanda J. Bischoff, Brandon M. Nelson, Zachary L. Niemeyer, Matthew S. Sigman, and Mohammad Movassaghi
J. Am. Chem. Soc.,
2017, 139 (43), pp 15539–15547; DOI: 10.1021/jacs.7b09541
10/2017
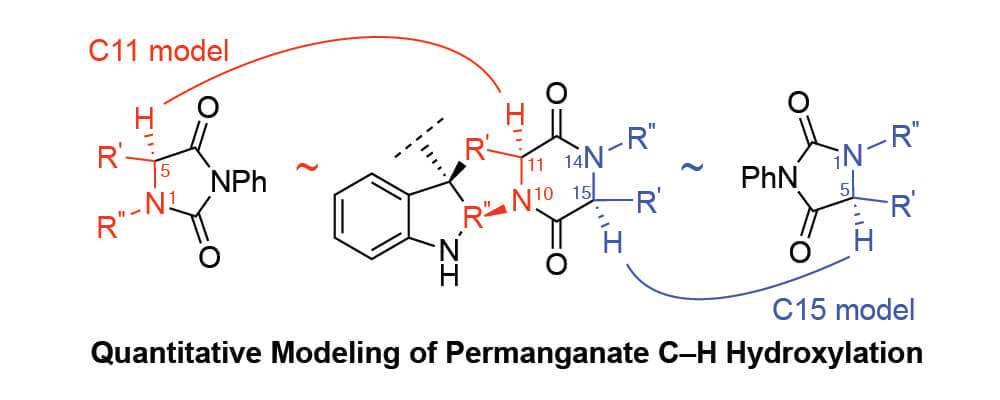
The bis(pyridine)silver (I) permanganate promoted hydroxylation of diketopiperazines has served as a pivotal transformation in the synthesis of complex epipolythiodiketopiperazine alkaloids. The Movassaghi group uses this late-stage C–H oxidation chemistry to strategically access N-acyl iminium ion intermediates necessary for nucleophilic thiolation of advanced diketopiperazines en route to potent epipolythiodiketopiperazine anticancer compounds. In this collaborative study, the Movassaghi and Sigman groups develop an informative mathematical model using hydantoin derivatives as a training set of substrates by relating the relative rates of oxidation to various calculated molecular descriptors.
The model prioritizes Hammett values and percent buried volume as key contributing factors in the hydantoin series while correctly predicting the experimentally observed oxidation sites in various complex diketopiperazine case studies. Thus, a method is presented by which to use simplified training molecules and resulting correlations to explain and predict reaction behavior for more complex substrates. The model that was developed using their designed hydantoin training set accurately predicted at least 12 of the 14 potential sites of oxidation in far more complex diketopiperazine substrates. The model offers a roadmap to synthetic design and application of this late-stage oxidation reaction in complex synthesis and provides a strategic guide into mapping other site selective oxidation processes.