General and Practical Potassium Methoxide/Disilane-Mediated Dehalogenative Deuteration of (Hetero)Arylhalides
Xin Wang, Ming-Hui Zhu, David P. Schuman, Dayou Zhong, Wen-Yan Wang, Lin-Yang Wu, Wei Liu, Brian M. Stoltz, and Wen-Bo Liu
J. Am. Chem. Soc.,
2018, 140 (35), pp 10970–10974; DOI:10.1021/jacs.8b07597
08/2018
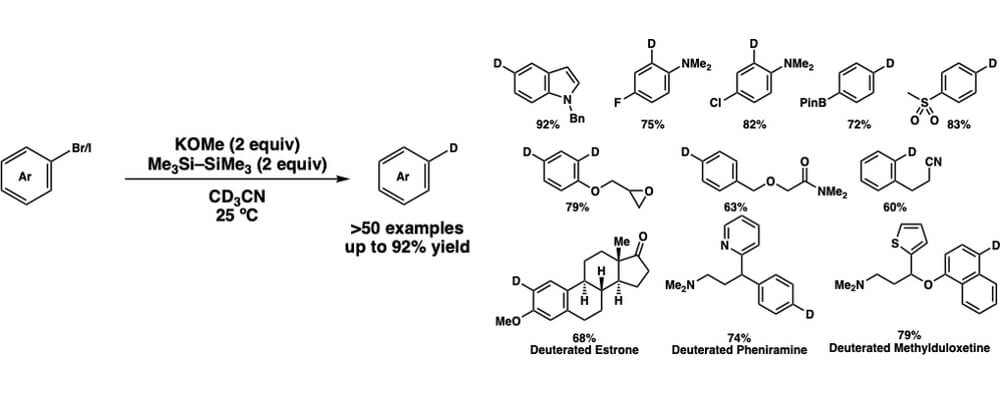
The use of deuterium labeled compounds, where a hydrogen is replaced with deuterium, has found widespread use in chemistry, pharmaceutical, and related research. Some specific uses of these labeled compounds include; the investigation of reaction mechanisms, tracking specific molecules, and changing drug metabolism.
Deuterium labeled compounds were often made by first converting the substrate to a reactive species, often an organometallic reagent, and then treating with a deuterium source. This approach has a number of safety and environmental concerns, along with limited functional group compatibility. Recently a number of transition-metal-catalysts have been developed to achieve deuterium labeling which represents a significant advantage over previous methods but still uses heavy-metals.
Our method of deuterium labeling presented here uses a mild, low cost potassium base-mediator, and is operationally simple compared to many previous methods. We are able to convert a number of commonly used aryl halides to the corresponding deuterium labeled compound in good yield, without the use of heavy metals and with broad functional group compatibility. The findings were made by the collaboration between the Stoltz group at Caltech and the Wen-Bo Liu group at Wuhan University.