Speciation and decomposition pathways of ruthenium catalysts used for selective C–H hydroxylation
Cornelia Flender, Ashley M. Adams, Jennifer L. Roizen, Eric McNeill, J. Du Bois and Richard N. Zare
Chemical Science
2014, 5, 3309-3314; 10.1039/C4SC01050G
06/2014
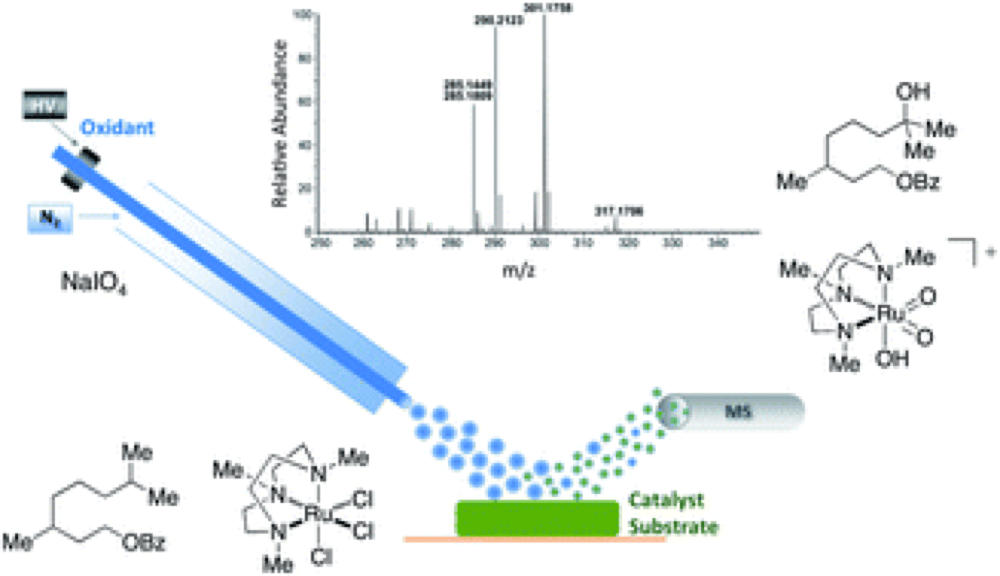
This collaborative project brings together the groups of Prof. Du Bois and Prof. Zare in order to provide a detailed insight into the mechanistic details of ruthenium-catalyzed C–H hydroxylation.
Using the desorption electrospray ionization mass spectroscopy (DESI-MS) developed by the Zare group the studies provided direct evidence for the formation of a high-valent dioxo-Ru(VI) species, previously predicted to be the active oxidant.
The sensitivity of the technique also allowed the identification of a number of unexpected Ru-oxo intermediates, a number of which may also function as competent hydroxylating agents.
The detailed picture of the intermediates involved in this reaction has provided an un-precedented level of detail of the reactive intermediates, highlights between reactivity differences in different catalysts and also leads on how the catalytic systems arrest.
The intermediates described in this study will inform the design and development of these catalyst systems.